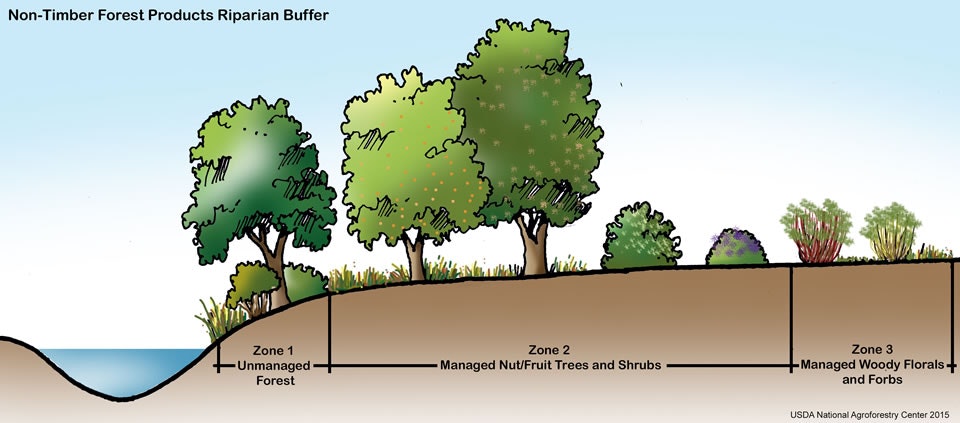
Riparian Forest Buffer
A riparian forest buffer is comprised of trees and other vegetation, such as shrubs and grasses, located next to a stream, river, or other body of water. These buffers act as a transition zone between the water and the adjacent land, helping to protect water quality and improve aquatic habitats by filtering pollutants and sediment from runoff. More benefits include:
- Bank stabilization and erosion control due to a complex root structure that holds soil in place.
- Flood resilience because of improved soil quality; trees are shrubs increase the organic matter and carbon levels in soil over time which contributes to a "soil sponge," which increases the infiltration potential and water holding capacity of the soil.
- Improved water quality as a result of increased surface water filtration during runoff events such as irrigation, heavy rain, and flash flooding.
- Increased habitat and food sources for wildlife, especially in forest buffers with a diversity of trees, shrubs, and forages.
Attached here is the spec sheet from the National Resource Conservation Service (NRCS), detailing the practice standards:
Riparian_Forest_Buffer_391_CPS_10_2020.pdfLinked below is a fantastic, quick video introduction to riparian forest buffers:
Here are some photos of various successful riparian forest buffers:

Credit to the USDA Forest Service
Credit to the USDA Forest Service


